
Why Become a Sports Vision Optometrist?
Sports vision optometrists work with patients at all levels, including [...]
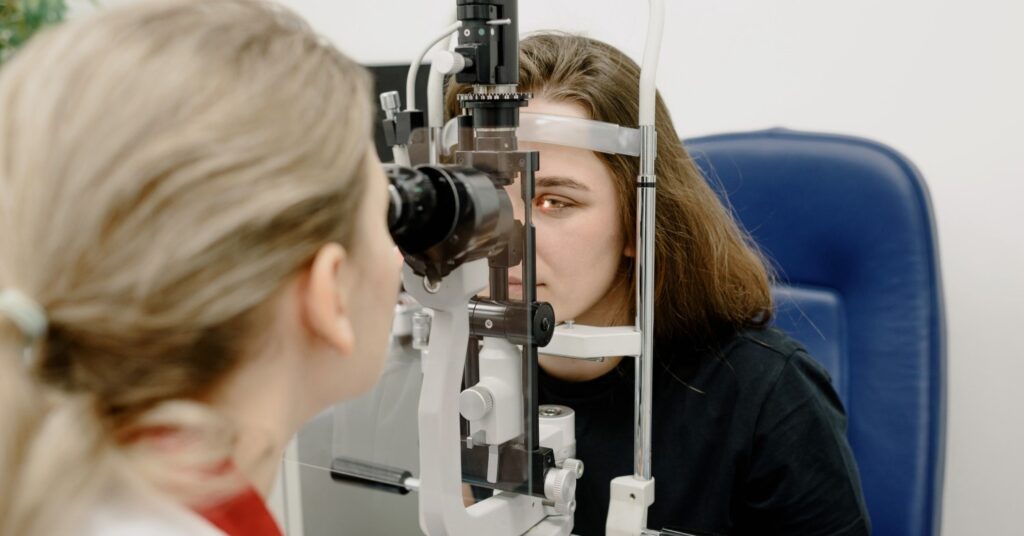
Opticians, optometrists, and ophthalmologists occupy different roles within the field of eye care. Each focuses on patient care but also demands unique qualities and requires its own training and education regimen.
Opticians are trained technicians who help fit eyeglasses and contact lenses with prescriptions provided by optometrists and ophthalmologists, but they don’t provide prescriptive or diagnostic services to patients. Ophthalmologists are physicians with eight years of medical school training who are licensed to diagnose and treat disease, prescribe medications, and perform eye surgeries to correct problems like cataracts. Optometrists hold a Doctor of Optometry (OD) degree, but don’t perform eye surgeries. They provide comprehensive patient care and diagnose eye disease, treat maladies and infections with medications, and prescribe corrective lenses to help improve patients’ vision.
Optometrists and ophthalmologists can specialize in specific age groups in specializations like geriatric eye care or pediatric eye health. They can focus their practice on diseases like glaucoma or macular degeneration, or specific areas of the eye like the retina or cornea. They also can identify and diagnose health issues beyond vision defects and abnormalities by identifying symptoms of diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, or even brain tumors.
If you’re interested in exploring a career in optometry, you may be wondering what it takes to succeed in this field. This article details the top 6 optometry skills and covers the following:
So what are the most valuable skills needed for a successful career in optometry? Let’s look at some of the qualities that are important for an optometrist and how they contribute to a thriving practice.
In the healthcare field, optometrists are less feared than dentists, but both professions work close to patients. Your interaction with people requires you to maintain a calm, professional manner and feel comfortable with close contact. This amicable manner should extend to all of your professional interactions, including those with office staff and colleagues.
Communication skills are a crucial component of customer care and medical follow-ups. Optometrists educate patients on important details of everyday vision care, ocular health and hygiene, and specific treatment for injury or disease. They also need to communicate clearly with other specialists when making referrals or obtaining more information or professional advice on a patient’s condition. Good communication with other staff members helps any practice run smoothly and keeps patients appropriately informed about their treatment and any issues they may encounter.
Language skills are key to good interpersonal communication. The ability to speak and write in more than one language is even more helpful when working with patients from different backgrounds and communities. Many bilingual practitioners find that fluency in another language qualifies them for more job offers and higher pay in certain regions of the US and many major metropolitan areas.
Good decision-making is a reflection of a practitioner’s competency and facilitates a thoughtful process regarding a patient’s treatment. Decisions must be made on how to proceed with treatment plans after a diagnosis, whether to consult a colleague about imaging or when is the optimal time to expand the business. Clear thinking on both medical and business decisions helps keep small and large practices running smoothly.
Problem-solving skills are a significant part of clinical reasoning when diagnosing eye conditions and formulating appropriate treatment plans. As healthcare providers, optometrists rely on their knowledge and training to remedy even the most complicated cases with solid assessment, planning, and care. For practitioners running their own offices, problem-solving skills come in handy when negotiating insurance coverage, billing, and staffing issues.
Good time management skills and accurate scheduling for a self-employed optometrist in private practice make for an organized work environment. Time management is important in larger practices and in hospital settings as well, where individuals rely on efficiency in exam rooms and with follow-up paperwork and communication. Training and experience inform how much time to allow for an eye examination, refraction, or a contact lens fitting, and to keep schedules and appointments on track.
A host of hard skills are required to provide ophthalmic and optometric care. Both require years of academic, technological, clinical, and medical training for diagnostic testing, testing for visual acuity, and vision correction procedures like Lasik surgery. Training focuses as much on anatomy as on patient care and business skills—all of which inform and provide structure for a successful career path.
Ideally, you should hold a bachelor’s degree in biology, chemistry, or pre-med, as these majors prepare you for taking the Optometry Admissions Test (OAT) and provide the academic foundation for your subsequent four-year course of study earning your Doctor of Optometry (OD) degree. The first two years of a DO degree cover fundamentals and clinical experience, then progress into patient care and preparation for sitting the first board exam for certification. Training then moves to rotations and internships. At the end of the fourth year of study, students are ready to sit for final board certification and graduate with a Doctor of Optometry degree.
The knowledge and hard skills you’ll acquire in a Doctor of Optometry program include learning about cell biology, ocular anatomy, and physiology, as well as performing refractions, lensometry, and visual acuity tests. You’ll also come away with training in patient care, ophthalmic business and management policy, public health, and clinical practice. These skills support a professional career and create a strong practice.
Doctor of Optometry programs like the one offered at the New England College of Optometry follow a prescribed path from start to completion. The school describes Year One as the time to establish the fundamentals, then deepen learning in Year Two while working in patient care. Field observations, lectures, and hands-on experience are all part of the training, and Year Three helps prepare students for the first board exam. Year Four provides the opportunity for students to experience full practice with four full-time clinical rotations in primary care, advanced care, specialty care, and an elective choice. This last year of training prepares students to take the final board exam and apply for a license or enter a residency. With a completed Doctor of Optometry degree and licensure in hand, graduates are ready to launch their careers.
Pursuing your optometry degree takes four years of full-time study. These four years build on the four years you’ve spent earning a bachelor’s degree in biology, chemistry, or pre-med. Some optometry program graduates decide to take an extra year-long residency program to specialize in a particular area, like cornea and contact lens, ocular disease, pediatric optometry, primary care optometry, and vision rehabilitation. (In addition, some programs offer an accelerated track for physicians and scientists who already hold a doctorate degree or equivalent.)
Applicants for the optometry doctorate program must pass the Optometry Admission Test (OAT), which assesses students in four subject areas: science, physics, quantitative reasoning, and reading comprehension. Successfully passing this exam is the first step in applying to any Doctor of Optometry program. Some programs may ask for GRE or MCAT scores as well.
If you haven’t already done so in your undergraduate studies, you must complete prerequisite coursework in biology, chemistry, physics, organic chemistry, biochemistry, microbiology, calculus, statistics, psychology, and English. Some programs accept one class in each, but others want two in select areas of study.
Curriculum at DO programs vary, but generally all coursework is similar to the New England College of Optometry’s four-year program. Early coursework includes cell biology and ocular anatomy, clinical reasoning, genetics, clinical medicine, the neural basis of vision, and color vision. Classes advance to cover vision development, public health, advanced surgical and laser procedures, ophthalmic business and management policy, and solving complex refractive issues. All coursework puts theory into practice by way of direct patient care and clinical rotations during the last year of studies.
Each state has its own set of licensing requirements and scope of practice. The most accurate way to find your state’s specific licensure requirements is to contact the state licensing board.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) lists the median annual income for optometrists as $124,000. Top earners work in physicians’ offices, while those in optometry offices earn about 20 percent less. The top ten percent of optometrists earn around $192,000.
You cannot earn an OD entirely online, as in-person clinical rotations are a vital component of any Doctor of Optometry program. However, hybrid programs, like the one launching in Fall 2023 at the New England College of Optometry, allow you to take your coursework online and arrange for you to undergo clinical rotations in an approved and appropriate setting close to where you reside.
Questions or feedback? Email editor@noodle.com

Sports vision optometrists work with patients at all levels, including [...]

Future health professionals considering the field of eyecare may well [...]

Roughly one in four optometry students pursue a residency after [...]

Forensic optometrists employ optometric science to assist the police in [...]

Ocular disease optometrists specialize in the early detection, diagnosis, and [...]
Categorized as: Optometry, Nursing & Healthcare